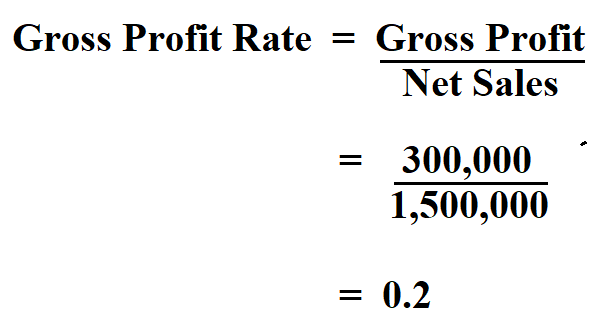
On the income statement, the gross profit line item appears underneath cost of goods (COGS), which comes right after revenue (i.e. the “top line”). If you offer discounts for bulk purchases, this can affect your gross profit percentage as volumes change. While gross profit is a useful high-level gauge, companies often need to dig deeper to understand underperformance.
What are the limitations of the gross profit ratio?
We will first use the above data to calculate the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Interpreting the Gross Profit Margin
- Gross profit percentage impacts pricing strategies by helping you determine if your pricing covers production costs and desired profit margins.
- A company might have low gross profit because it has high production costs.
- Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
- It’s helpful for measuring how changes in the cost of goods can impact a company’s profits.
- However, businesses aim to achieve a gross profit margin that ensures profitability while remaining competitive in their specific market.
It’s a metric that should be evaluated within the broader context of your company’s financial performance. Gross margin is the percentage of profits an organization is able to retain after all deducting all direct expenses relating to production. To understand the sales gross margin formula, it is important to understand a few other concepts around it such as gross sales, cost of goods sold, and net sales. The gross profit margin (also known as gross profit rate, or gross profit ratio) is a profitability metric that shows the percentage of gross profit of total sales. As you continue to refine your approach to calculating and leveraging gross profit percentage, you’ll develop a more nuanced understanding of your business’s financial dynamics. This knowledge will empower you to make more informed decisions, optimize your operations, and ultimately drive sustainable growth for your company.
How To Calculate Gross Profit Margin

When assessing a good gross margin, avoid comparing across industries and instead compare companies of similar size in the same industry. So essentially, gross profit measures the profitability of a company’s production and manufacturing processes, while net profit measures the company’s profitability as a whole. The 2 metrics are different, but both are valuable in assessing a company’s ability to generate profit. The 2 components of gross profit—revenue and cost of goods sold—each offer an opportunity to examine business strategy.
Even products that sell a large volume may not be very profitable if they demand a large amount of materials and labor costs. Assess which products deliver the best profit and consider whether you could cut poorly performing products and focus on more profitable ones. Gross profit margin is a type of profit margin where the cost of goods sold is subtracted from total revenue. It’s the most straightforward measure of profit margin and shows how much money a company retains after accounting for the cost of the goods. Determining what constitutes a “good” gross profit margin is not a one-size-fits-all proposition, as it varies by industry, business size, and economic conditions.
Gross Profit Ratio: Definition
It measures the overall effectiveness of management in relation to production/purchasing and pricing. Remember, while profit percentage is crucial, it should be considered alongside other financial metrics like revenue growth, cash flow, and return on investment. The most successful businesses take a holistic view of their financial performance, using profit percentage as one of several key indicators guiding their strategy. A gross income amount is reported on a company’s profit-and-loss statement and is typically a standardized calculation for businesses in the same industry. If not managed properly, these indirect costs can really eat into a company’s profit.
Finally, compare your gross profit margins against your direct competitors. If you find they report significantly higher gross margins, consider what they might be doing differently and whether it could apply to your company. Although you might not be able to match them in size or volume of product sold, you may discover they’re purchasing materials from a more affordable vendor. By subtracting its cost of goods sold from its net revenue, a company can gauge how well it manages the product-specific aspect of its business.
Both ratios provide different details about a business’ performance and health. Using a gross margin formula calculator helps an organization to understand their production costs and basic financial health derived through their core activities in percentage format. A high gross margin 2019 volunteer mileage rates and irs reimbursement guidelines indicates that the company might be able to retain more capital. To determine gross profit, Garry would subtract COGS ($650,000) from his total revenue ($850,000). For gross profit, he would ignore the administrative costs and salary costs on his company’s income statement.
Net profit calculations include revenue and Cost of Goods Sold, as well as fixed costs like Administrative Costs and Salary. Net profit also includes all other expenses involved in running a business, such as advertising costs and taxes. It can be thought of as the proportion of sales over the direct costs incurred in producing the good. Raw materials and direct labour make up the majority of these direct costs, also known as COGS. As a result, the gross profit is divided by the total sales stated in percentage terms to arrive at the gross profit percentage formula.
